Regardless of whether you are currently employing an email marketing approach and require management’s buy-in to enhance your strategy, or if you are entirely new to the subject and need to emphasize the significance of email, it is imperative to consider the following crucial steps.
First Step: Defining Email Marketing
The interpretation of email marketing can vary greatly among individuals. While some may associate it with the practice of renting lists from third parties, others view it as a means of nurturing relationships with existing contacts to drive sales and enhance customer retention. In the context of this document, email marketing is defined as the latter.
Second Step: Establishing Goals
It is vital to effectively convey the purpose of email marketing within your organization. By beginning with a clear goal, others will be able to comprehend how it aligns with the overall business strategy.
Third Step: Building Your List
Your contacts serve as the cornerstone of your strategy, as you are essentially constructing a plan revolving around engaging with them. Your objectives are closely linked to their actions. Consequently, your lists play a pivotal role in the puzzle. Successful email marketing hinges on delivering relevant content, thus your plan should encompass extensive knowledge acquisition about your contacts.
Fourth Step: Organizational Structure by Department or Group
How many individuals within your organization will utilize email marketing? Is it solely for corporate communications or will the public relations team also employ it? What about the web group, product marketing, or channel marketing? This toolkit will provide guidance to facilitate organization, enabling marketing to maintain some level of control over the consistency of all communications.
Fifth Step: Content Planning
One of the primary reasons newsletters become defunct is the challenge of generating content within the given deadline. It is imperative to create an editorial calendar for your newsletters and have it readily available alongside your proposal.
Sixth Step: The Bottom
Line Numbers hold a significant appeal. It is crucial to be prepared to discuss the return on investment (ROI) and the metrics that will be employed to gauge the success of your email marketing strategy.
First Step: Defining Email Marketing
Before commencing the development of your email marketing strategy, it is imperative to establish the precise significance of email marketing for your organization. Taking into consideration the potential existence of email marketing in 1828, when Noah Webster initially published his American Dictionary of the English Language, the definition could conceivably have been as follows:
Email marketing: The utilization of email as a means to convey consent-based communications with the objective of cultivating relationships, augmenting sales, and enhancing customer retention.
The crux of the aforementioned definition lies in the aspect of consent. While it is plausible that your organization may also opt to rent or acquire contact lists to expand its operations, this particular document will exclusively concentrate on strategies pertaining to consent-based or internally compiled lists. Numerous organizations have come to comprehend that, despite the fact that the process of constructing an internally compiled list may necessitate a greater investment of time, it promptly demonstrates its value.
The definition also alludes to customer retention. Email is unequivocally the most prevalent medium employed to maintain contact with existing customers. By furnishing them with valuable information and updates tailored to their individual interests, email facilitates the cultivation of a relationship between the organization and the customer.
Nevertheless, there exists a far more profound definition of email marketing: the interpretation it holds in the context of your specific enterprise. Clearly defining the purpose of email marketing for your organization is of paramount importance, as it will serve as the impetus guiding all subsequent email-related endeavors.
Second Step: Establishing Goals
Marketing Sherpa, a publisher that specializes in case studies and research on internet marketing, published an article in early 2005 addressing the top five frustrations encountered in email marketing. The fifth frustration identified was the lack of recognition and value attributed to email by management. Email is often regarded as a tactical and cost-effective means of engaging prospects and customers to drive sales or increase website traffic. However, this perspective is limited and fails to consider the broader implications. By developing a well-structured strategy, organizations can establish clear expectations for long-term success and effectively address these frustrations.
Therefore, it is crucial to answer the following key question: What is the purpose of email marketing for your organization? Additionally, it is essential to address other important queries, such as why email marketing is chosen, how it will contribute to existing marketing efforts, and how it will integrate with overall marketing strategies. Furthermore, organizations should evaluate their current lead generation process and determine how email marketing can enhance it. It is also important to consider whether regular communication with customers already exists and whether email marketing will replace or complement other communication strategies.
If uncertainty persists, examining examples of how different organizations utilize email marketing can be helpful. For instance, the non-profit Audubon Nature Institute tailors newsletters to specific audiences, including members, non-members, and community leaders. The member newsletter focuses on providing unique content that validates membership, while the non-member newsletter aims to drive additional traffic to the various parks. The leader newsletter communicates activities resulting from donations.
Similarly, e-commerce vendor Lydia’s Uniforms strategically employs newsletters and email alerts to boost online sales, but they planned ahead by determining the type of information they would collect to segment their audience based on various fields. They utilize customer preferences for brands or products to send targeted promotions. The provision of highly relevant content has undeniably contributed to their overall success.
The Analysis of Lead Generation and Sales Cycle
At the utmost level, there are typically two distinct groups of individuals with whom you will engage in communication: customers and non-customers. As a component of your lead generation procedure, the electronic mail newsletter can assist in establishing a strong connection with the non-customer or potential client. By delineating the systematic approach of your organization, you can identify areas of potential opportunities.
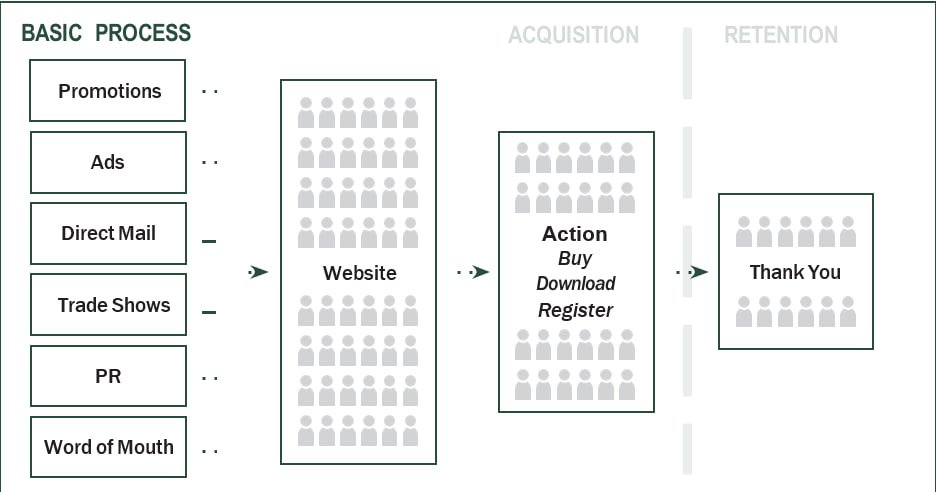
This diagram presents a straightforward depiction of a lead generation process that excludes the utilization of email marketing. It portrays the arrival of visitors to the website and subsequent engagement in a specific course of action. Currently, the only form of follow-up is a Thank You page that may display a receipt or confirmation.
Let us now proceed to identify certain shortcomings associated with this process.
• Web-centric approach – there is a lack of effort directed towards customer retention, resulting in a highly transactional approach.
• Missed opportunity – there is an absence of data collection for individuals who do not immediately take action. What about those individuals who are conducting research and wish to acquire further knowledge about your offering or industry?
On the subsequent page, we will examine a scenario wherein email marketing is integrated into the process.
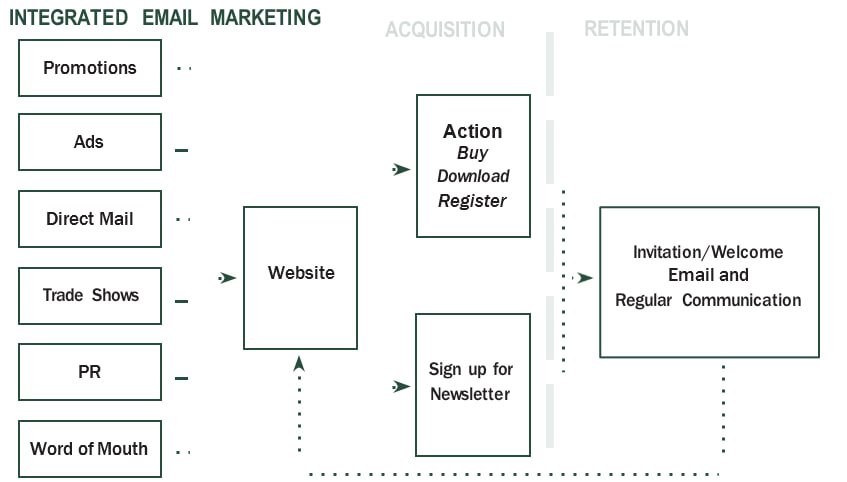
The aforementioned diagram serves as a reflection of the preceding illustration; however, it elucidates the simplicity with which one can employ an electronic mail newsletter to procure potential customers who are merely engaging in exploratory research during their visit to a website.
Lead Acquisition
The process of acquiring leads involves capturing prospects through the newsletter sign-up form, even if they are not yet ready to take further actions. By creating a newsletter or other form of communication specifically for this audience, it becomes possible to initiate the development of a relationship with them. This relationship-building can eventually lead to sales or other desired actions in the future. It should be noted that without this regular communication, the contact may easily forget about your organization as soon as they leave the website.
Customer Retention
In terms of customer retention, for those individuals who do take a desired action on the website, the process now includes sending them a welcome email. This email serves as an invitation for them to remain in touch with your company.
Additional advantages of incorporating email marketing into the process of generating potential leads and the sales cycle encompass the following:
Opportunities for viral marketing that facilitate word-of-mouth promotion
Receiving feedback through tracking reports, which provides valuable information on the levels of interest
Strengthening of brand identity through consistent communication
Ability to engage with customers and prospects based on their previous interactions
Enhanced customer loyalty resulting from regular communication
Increased website traffic as a result of email marketing
Third Step: Building Your List
Effective email marketing begins with a well-curated list. As per the fundamentals of Marketing 101, it is imperative to have a profound understanding of our target audience. Are you familiar with the ins and outs of your current list? Dedicate a moment to assess the information you possess and develop a strategic approach to acquire additional data progressively. The more comprehensive your knowledge of your subscribers, the more seamless it will be to furnish them with valuable content through your communications. For the purpose of illustration, our hypothetical company’s existing lists exhibit the following attributes:
| List Name | Source of List | Permission? | Status | Known Fields |
| Customers | CRM | Yes | Exported and ready | name, address, phone, email |
| Product A Prospects | Trade Show | No, need to invite | Spreadsheet, ready | name, email |
| Interested Prospects | Website | Yes | Text file, ready | |
Consider reflecting on the data available to you and the desired knowledge you seek regarding potential prospects and customers. The following categories encompass typical information:
Demographics (such as marital status, income, and location)
Areas of interest (whether it be product A or B, specific services, or valuable information)
Quantitative measures such as purchase amounts or donations
Relevant business information (including industry and title)
Time frame for decision-making
Budgetary considerations
The exceptional capability of email marketing software lies in its capacity to segment contacts based on existing information, enabling the dissemination of targeted and personalized messages.
Data Collection at the Right Time
Determining the appropriate timing for data collection is a crucial step once you have identified the type of data you possess and the data you require. It is imperative to consider when exactly this information should be collected, taking into account the specific audience you are targeting in order to avoid overwhelming customers with excessive inquiries upfront. In addition to the initial data collection, there are several other instances where information can be gathered:
Requesting additional information on the Thank You page after subscription.
Integrating a survey within the confirmation or welcome email.
Incorporating survey questions at various points throughout the newsletter’s lifespan.
Encouraging subscribers to periodically update their information.
Planning for a Growing Email List
A crucial aspect of any email marketing strategy involves developing plans to continually expand the email list. Here are some proposed tactics to promote each newsletter:
Incorporate a “forward to friend” option in all outgoing emails.
Place a newsletter sign-up form prominently on the website.
Direct all potential customers to the website through advertising efforts.
Gather email addresses during the checkout process at retail stores, if applicable.
Implement a newsletter opt-in feature during the e-commerce checkout process on the website.
Collect email addresses at trade shows and other events.
Include the website on all essential company documents, such as stationary and business cards.
Promote the newsletter(s) and website through the hold music for incoming calls.
Train customer service representatives to inquire if callers would like to receive the newsletter.
Train support staff to inquire if callers would like to receive the newsletter.
Include a link to the newsletter sign-up form in email signatures for all employees, particularly those in support and customer service roles.
If you currently have no email list and are starting from scratch, we recommend the following:
Append email addresses to your existing prospect/customer database.
Begin collecting email addresses from the website.
Fourth Step: Organizational Structure by Department or Group
Thus far, we have examined the objective behind email marketing and have explored its potential in complementing existing marketing endeavors while also serving as a means of capturing new leads and fostering relationships. With a solid understanding of your target audience, the subsequent step in developing your email marketing strategy involves internal organization.
Once you have outlined how email marketing aligns with your own processes and have identified your target audience, you will begin to discern numerous opportunities for organizing the information in order to achieve your initial objectives.
The implementation of a concise communication chart will not only facilitate comprehension of the role played by each external communication but will also provide insight into the resources necessary for creating each element.
Fifth Step: Content Planning
Once you have determined the target audience and established the desired form of communication, it is essential to strategize the actual substance of each message. To facilitate this process, it is recommended to create an editorial calendar. This will enable you to plan ahead and guarantee that each communication conveys pertinent information.
The potential of email is boundless. However, it is crucial to bear in mind the primary purpose of these messages: to provide value to your recipients. Do not simply distribute content for the sake of distributing it to a predetermined list of individuals.
Sixth Step: The Bottom
In order to effectively carry out any critical marketing function, it is imperative to establish a set of metrics that will determine the level of success achieved. For each type of publication, it is essential to clearly outline the indicators that will signify success. By sharing these metrics, all stakeholders involved can better understand the true impact that email marketing can have on the organization. Here are several suggestions for metrics that can be utilized:
Email Marketing Reports
Open Rate – This metric provides a general gauge of interest by measuring the number of messages that have been opened.
Conversions by source – This metric focuses on the number of individuals who have taken a specific action as a direct result of the message they received.
Click-Through Rate – By quantifying the number of individuals who have clicked on a link within the message, this metric serves as an effective measure of interest and activity.
Forward rate – This metric quantifies the number of times the message has been forwarded to others, allowing for the measurement of viral marketing or the creation of buzz.
Business Metrics
The tracking of leads from email forwarding or referral is crucial in order to assess the effectiveness of different sources in generating leads.
It is essential to analyze sales metrics both before and after implementing email marketing strategies to identify any trends or improvements in sales performance.
Examining website traffic before and after email marketing campaigns is important to gauge the impact of such campaigns on increasing website visits.
It is noteworthy to analyze website traffic on the day an email is sent out as it provides insights into the immediate response and engagement of recipients.
Assessing customer retention rates before and after implementing email marketing initiatives allows for an evaluation of the effectiveness of these initiatives in retaining customers.
Evaluating the conversion rate from email before and after initiating email marketing efforts helps determine the impact of these efforts on converting leads into customers.
Benchmarking
Bronto.com actively monitors the average open and click-through rates for all customers. If you are interested in comparing your own metrics against industry averages, please feel free to contact us to find out more information.

