Menu
The Purpose of this paper is to overview the Inventory management in supply chain and their current Inventory related issue in a present day business and present a conceptual methodology for related issue. The methodology based on the inventory, which are inputs for the methodology and benefits which are output of methodology.
A literature review is conducted on management or control of inventory and also issues related to inventory in industry, and its various parameters. A conceptual methodology for inventory issues in present business.
The scope of inventory management concerns the fine lines between replenishment lead time, carrying costs of inventory, asset management, inventory forecasting, inventory valuation, inventory visibility, future inventory price forecasting, physical inventory, available physical space, quality management, replenishment, returns and defective goods, and demand forecasting. Balancing these competing requirements leads to optimal inventory levels, which is an ongoing process as the business needs shift and react to the wider environment.
Inventory is the raw materials, work-in-process products and finished goods that are considered to be the portion of a business’s assets that are ready or will be ready for sale. Inventory represents one of the most important assets of a business.
The paper makes an attempt to understand the importance of inventory, Inventory issue and then to present a conceptual methodology for inventory issue.
The objective of this paper are:
The paper is organized as after the literature review a conceptual methodology for inventory related issue is presented. Finally, concluding remarks with some directions for future research are provided.
Inventory Management is the part of Supply chain management that plans, implements and controls the efficient, effective, forward, and reverse flow and storage of goods, services, and related information between the point of origin and the point of consumption in order to meet customer’s requirements.
Inventory management is defined as “the continuing process of planning, organizing and controlling inventory that aims at minimizing the investment in inventory while balancing supply and demand”. Specifically, the process is a supervision of supply, storage and accessibility of items in order to ensure an adequate supply without excessive oversupply.
Since the mid-1990s, there has been a large increase in annual number of inventory management articles. Researchers conduct such relevant research in several respects. First, most of publications in logistics journals are about traditional inventory control models. These papers evaluate traditional inventory control models under particular conditions or incorporate additional considerations into established models. Another popular theme is about developing approaches to reduce the quantity of inventory that a warehouse must have, which refers to reducing the safety stock by centralization of warehouse locations.
Supply Chain is defined as a system of organizations, people, activities, information, and resources involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer. Supply chain activities involve the transformation of natural resources, raw materials, and components into a finished product that is delivered to the end customer.
The network of organizations that are involved, through upstream and downstream linkages, in the different processes and activities that produce value in the form of products and services delivered to the ultimate consumer. A set of firms that pass materials forward. The alignment of firms that brings products or services to market including the final customers as part of the supply chain. A set of three or more entities (organizations or individuals) directly involved in the upstream and downstream flows of products, services, finances, and/or information from a source to a customer. Inventory is part of supply chain or supply chain management whose totally focus on management of inventory from supplier to customer and vice versa.
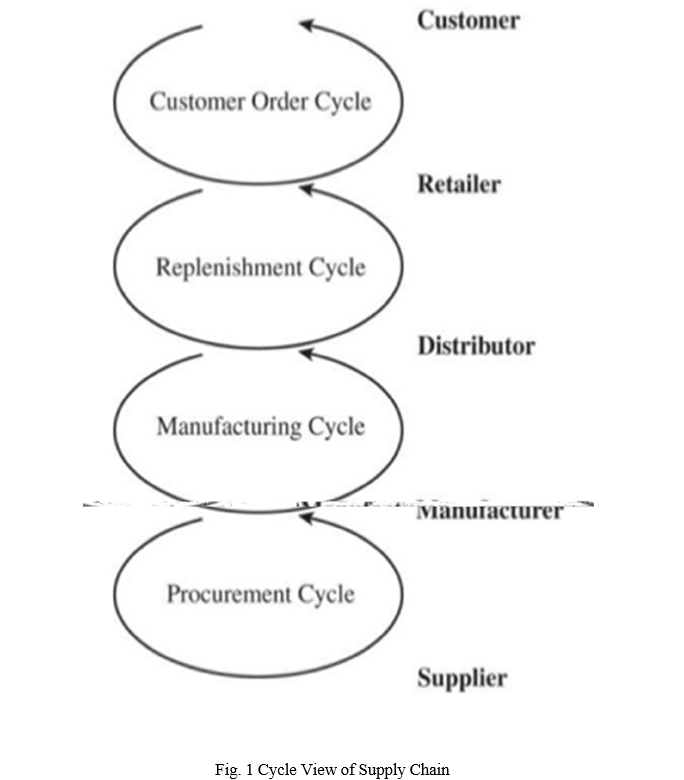
Cycle view – In which the processes in a supply chain are divided into a series of cycles, each performed at the interface between two successive stages of a supply chain as show in below Fig.1.
Push/Pull view – In which the processes in a supply chain are divided into two categories depending on whether they are executed in response to a customer order or in anticipation of customer Pull processes are initiated by a customer order, whereas push processes are initiated and performed in anticipation of customer orders.
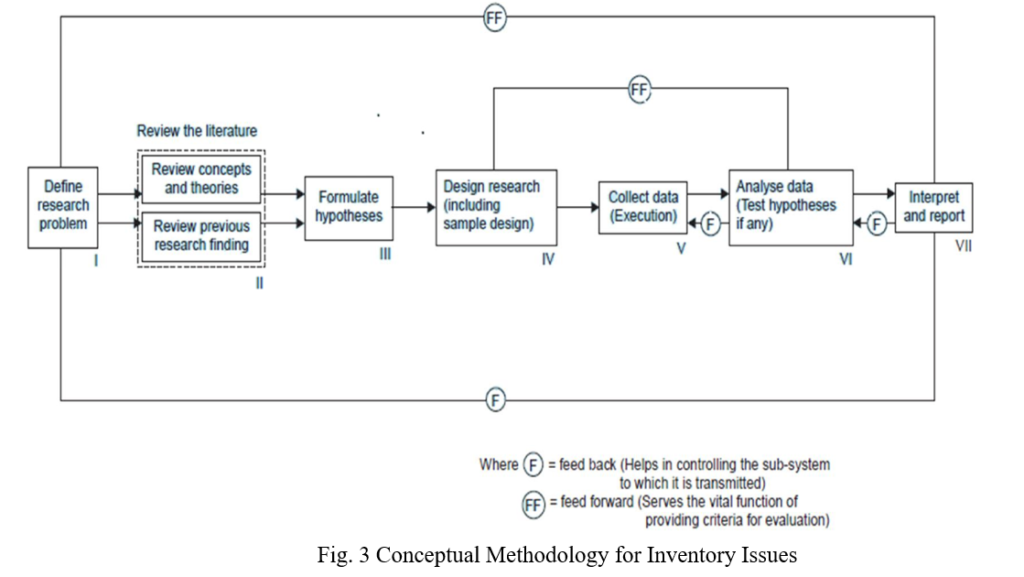
The paper presents a conceptual methodology for Inventory issue. The key logistics issue is here mentioned depending its internal or external inventory issue .It is expected that this methodology would be highly beneficial to the organizations in leveraging the efficiency of supply chain management. There is a need for an empirical validation of the proposed methodology. The bi-directional information at different levels will have affected the supply chain at all levels and it should be managed to reduce the information distortions.
Inventory is an important area where every company has to concentrate on and differentiate themselves with their competitors. With the growing demand for various varieties of products available all over the world people’s expectations are changing for every product. If a company wants to survive in the long run it should pay special attention to the area of supply chain and Inventory. Research is demanded to reduce the product cost and improve the quality with reduced failure rates.

Maadico is an international consulting company in Cologne, Germany. This company provides services in different areas for firms so they will be able to interact with each other. But specifically, raising the level of knowledge and technology in various companies and assisting their presence in European markets is an aim for which Maadico has developed … (Read more)