Artificial intelligence has been making significant advancements in various fields, such as diagnosing diseases, translating languages, and providing customer service, to name a few. The progress that AI has made is quite impressive, and it is understandable why some might fear that it could replace human workers. However, this is not necessarily going to be the case. We have never before had digital technology that is so responsive to our needs, nor have we ever been so responsive to our tools. Although AI will undoubtedly revolutionize the way work is done and who does it, its primary impact will be to complement and enhance human capabilities, rather than to replace them.
Incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) to automate business processes has become a common practice for many companies. However, those that solely rely on AI to replace human employees will only witness short-term gains in productivity. Our extensive research, which involved studying 1,500 companies, revealed that businesses achieve the most significant improvements in performance when humans and machines work together. This is achieved through collaborative intelligence in which humans and AI actively enhance each other’s strengths and compensate for each other’s weaknesses. While humans excel in leadership, teamwork, creativity, and social skills, machines are better equipped for speed, scalability, and quantitative capabilities. It is essential to recognize that what humans find easy, such as making a joke, can be challenging for machines, whereas analyzing gigabytes of data is a task that remains virtually impossible for humans. To succeed in the business world, companies require both human and machine capabilities.
Collaboration is an essential asset that holds significant value in achieving success in various fields and industries.
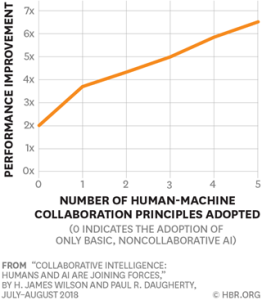
Companies can reap benefits by improving collaboration between human employees and artificial intelligence. To achieve this, they can follow five guiding principles. Firstly, they should rethink their business processes. Secondly, they should encourage experimentation and employee involvement. Thirdly, they should take an active role in directing their AI strategy. Fourthly, they should collect data in a responsible manner. Lastly, they should revamp their work practices to incorporate AI and foster related employee skills. A recent survey of 1,075 companies across 12 industries revealed that the more principles a company adopts, the more effective their AI initiatives are. This is reflected in improved speed, cost savings, revenues, and other operational metrics.
To fully capitalize on this collaboration, it is imperative for companies to comprehend the most efficient ways in which humans can augment machines, as well as how machines can amplify the strengths of humans. Additionally, it is essential for companies to reconfigure their business processes in order to facilitate this partnership. Our extensive research and practical experience has led us to develop comprehensive guidelines that can aid companies in achieving this objective, thereby unleashing the potential of collaborative intelligence to drive their businesses forward.
Assisting the mechanical apparatus with the aid of human intervention is a plausible scenario.
To fulfill the requirements of machine learning, humans are expected to execute three pivotal roles. Firstly, they must impart the knowledge to machines to accomplish specific tasks. Secondly, they should elucidate the results of such tasks, particularly when they produce unexpected or debatable outcomes. Finally, they are accountable for ensuring the ethical deployment of machines by, for instance, preventing robots from causing any harm to humans. These three fundamental roles are indispensable and must be executed with utmost diligence to achieve optimal results.
Training.
Machine-learning algorithms require an extensive amount of training in order to perform their designated tasks. This entails accumulating vast sets of data to educate machine-translation applications in the handling of idiomatic expressions, medical apps in detecting disease, and recommendation engines in aiding financial decision-making. Furthermore, artificial intelligence (AI) systems must be trained to interact with humans in the most effective manner possible. While organizations from various sectors are still in the early stages of filling trainer positions, prominent tech companies and research groups have already established experienced training staffs and possess a wealth of expertise. These organizations are equipped with the necessary resources and knowledge to further develop and enhance machine-learning algorithms, which in turn will lead to more efficient and innovative applications in the near future. The consistent utilization of these training techniques, coupled with the implementation of advanced technologies, will allow for the continued evolution and growth of machine-learning.
Microsoft’s AI assistant, Cortana, was developed with the intention of giving it a personality that exudes confidence, care, and helpfulness without appearing bossy. Achieving this required a significant amount of training and effort from a team comprising a poet, a novelist, and a playwright. Similarly, the development of the personalities of Apple’s Siri [1] and Amazon’s Alexa also necessitated the involvement of human trainers, who ensured that the assistants accurately represented their respective companies’ brands. Apple’s Siri, for instance, was given a hint of sassiness, which consumers might expect from the company. It is evident that creating an AI assistant with a personality that is relatable and engaging for users requires a significant investment of time, resources, and expertise. Nevertheless, the end result is an AI assistant that is not only efficient but also has a unique and well-defined personality.
AI assistants are currently undergoing training to exhibit more intricate and nuanced human qualities, such as empathy. Koko, a start-up that originated from the MIT Media Lab, has created innovative technology that can enable AI assistants to appear more compassionate. For example, if a user is having a difficult day, the Koko system does not simply respond with an automated message like “I’m sorry to hear that.” Rather, it may inquire for additional details and then provide guidance to help the individual view their problems from a different perspective. If the user is experiencing stress, Koko might suggest viewing that stress as a positive emotion that could be utilized to take action. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the way in which AI assistants communicate with users, enhancing the user experience and making the assistants more human-like.
Explaining.
As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes more prevalent, it is increasingly relying on opaque processes, otherwise known as the black-box problem. This poses a challenge as it requires human experts to explain the behavior of the AI to non-experts, otherwise known as explainers. In industries that rely on evidence-based decision-making such as law and medicine, explainers become particularly important. They help practitioners understand how the AI weighs inputs to make decisions such as medical recommendations or sentencing. Explainable AI is also important in industries such as insurance and law enforcement where it can help understand why an autonomous car made certain decisions that led to an accident. In regulated industries and consumer-facing industries where the output of machines could be challenged as unfair, illegal, or incorrect, explainers are becoming increasingly important. Thus, explainable AI will be crucial in ensuring that machines are accountable and transparent when making decisions that can have significant impacts on individuals and society as a whole. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of the European Union (EU) has granted consumers the privilege of requesting an explanation for any decision that is algorithm-based, such as the rate offer for a mortgage or credit card. This is a domain where the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) will play a significant role in generating more employment opportunities. According to experts, it is estimated that organizations will be compelled to create approximately 75,000 new job positions to manage the GDPR requirements.
Sustaining.
Enterprises require personnel who are capable of interpreting the results of AI, as well as “sustainers” who are responsible for ensuring that AI systems operate effectively, securely, and conscientiously on a continuous basis.
The implementation of Artificial Intelligence has the potential to enhance our capacity for analysis and decision-making, while also amplifying our creative potential.
A group of professionals, commonly known as safety engineers, specialize in projecting and mitigating potential harm caused by Artificial Intelligences. In particular, developers of industrial robots operating in collaboration with humans have taken meticulous measures to guarantee that these robots are able to identify human presence and avoid any potential danger. In situations where AIs have caused harm, such as in the case of an autonomous vehicle being involved in a fatal accident, these specialists may evaluate reports from explainers. The aforementioned experts play a vital role in ensuring the safety and security of individuals in the presence of AIs.
Other teams of supporters ensure that ethical standards are maintained by AI systems. In the event that an AI system for credit approval is discovered to be discriminating against specific groups of people, such as what has occurred in the past, these ethics managers are responsible for investigating and resolving the issue. Data compliance officers, who have a similar function, attempt to guarantee that the data utilized in AI systems conforms with GDPR and other consumer-protection laws. Another data-use position is to guarantee that AIs manage information in a responsible manner. These individuals also ensure that data is utilized in a way that is consistent with consumers’ privacy preferences. Through these efforts, AI systems can be made to operate in a more ethical and responsible manner.
Like many other technology companies, Apple leverages artificial intelligence (AI) to obtain personal information about users as they interact with the company’s products and services. The primary objective of utilizing AI is to enhance the user experience; however, unbridled data collection can jeopardize privacy, upset customers, and contravene the law. The “differential privacy team” at Apple is dedicated to ensuring that while the AI attempts to acquire as much knowledge as possible about a group of users in a statistical context, it is simultaneously safeguarding the privacy of individual users. This team’s commitment to user privacy is a testament to Apple’s dedication to providing a secure and pleasant user experience.
Machines Assisting Humans
Smart machines are contributing to the betterment of humanity in three distinct ways. Firstly, they are capable of enhancing our cognitive capabilities, thereby allowing us to achieve feats that were previously not possible. Secondly, these machines can engage with customers and employees, freeing us up for more complex tasks that require human intervention. Lastly, they can replicate human skills, thereby extending our physical abilities beyond what we are naturally capable of achieving.
Amplifying.
Artificial intelligence has the potential to enhance our cognitive and decision-making abilities by providing us with the relevant information at the appropriate time. However, it can also have a positive impact on our creativity. A prime example of this is Autodesk’s Dreamcatcher [2] AI, which has the ability to amplify the imagination of designers, even those who are already exceptional. When using Dreamcatcher, a designer can provide specific criteria for the desired product, such as a chair that can support up to 300 pounds, has a seat height of 18 inches, is made of materials that cost less than $75, and so on. Additionally, the designer can supply information about other chairs that they find aesthetically pleasing. Dreamcatcher then generates thousands of designs that meet those specific criteria, often sparking new ideas that the designer may not have initially considered. The designer can then guide the software, indicating which chair designs they prefer and which ones they don’t, leading to a new round of designs. This process can be repeated multiple times until the desired design is achieved. Ultimately, the use of AI tools like Dreamcatcher can lead to the creation of innovative and unique designs that would have been difficult to achieve otherwise. The potential of AI to enhance creativity in various fields is enormous, and its use is only expected to grow in the future.
Dreamcatcher executes numerous calculations during the iterative process to guarantee that every design proposal satisfies the designated requirements. This enables designers to focus on utilizing their professional judgment and artistic sensibilities, which are unique human attributes. Consequently, Dreamcatcher’s capabilities allow designers to produce designs that are not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing.
Interacting.
Human-machine collaboration offers companies the opportunity to engage with their employees and customers in innovative and highly productive ways. For instance, AI agents such as Cortana can assist with communication between individuals or even on behalf of individuals, like transcribing a meeting and sharing a voice-searchable version with those who were unable to attend. Such applications are inherently scalable and can be utilized to provide routine customer service to a vast number of people simultaneously, regardless of their location. This makes it possible for businesses to operate more efficiently, saving time and resources, while simultaneously improving the customer experience.
SEB, a prominent Swedish bank, has recently integrated a virtual assistant, named Aida, to engage with millions of customers. Aida is well-equipped to handle natural-language conversations and has access to a vast amount of data, enabling her to respond to frequently asked questions, such as opening accounts or making cross-border payments. Moreover, Aida can ask follow-up questions to resolve customers’ issues and analyze their tone of voice, using that information to offer better service in the future. Aida transfers the caller to a human customer-service representative in the event that the system cannot address their concern; this happens in approximately 30% of cases. The call is then monitored to learn how to resolve similar issues in the future. With Aida handling the fundamental requests, human representatives can focus on resolving more complex issues, particularly from unhappy callers who may require extra assistance. This integration of Aida represents a significant advancement in customer service, enabling SEB to provide prompt and efficient assistance to its customers.
Embodying.
Artificial intelligences such as Aida and Cortana primarily exist as digital entities; however, in certain instances, the intelligence is incorporated within a robot that enhances human work processes. AI-powered machines possess advanced sensors, motors, and actuators and can now identify individuals as well as objects and work safely in unison with humans in environments such as factories, warehouses, and laboratories. The ability of AI technology to complement human performance and augment our capabilities has enabled us to achieve greater productivity and efficiency in our daily lives.
In the field of manufacturing, robots are undergoing a transformation from their previous state as potentially hazardous and unintelligent industrial equipment to a more intelligent, contextually-aware form, termed “cobots.” A cobot’s arm may be used to perform repetitive tasks that necessitate significant physical exertion, while a human worker performs tasks requiring dexterity and human judgment, such as the assembly of a gear motor.
Hyundai is broadening the scope of cobot concept by incorporating exoskeletons into their repertoire. These innovative wearable robotic devices have the ability to adjust to the user and environment in real time. As a result, industrial workers will now have the capability to perform their work with exceptional strength and stamina beyond human limits.
Redesigning your business
In order to fully optimize the potential of AI, it is essential to restructure operations. This can be achieved by identifying and defining an operational area that has the potential for improvement. This area could be an internal process that has been hindering progress, such as HR’s tardiness in filling staff positions. Alternatively, it could be a long-standing problem that was previously unsolvable but can now be tackled using AI, such as identifying adverse drug reactions across diverse patient populations. Furthermore, there are several innovative AI and advanced analytic techniques that can bring to light issues that were previously invisible, but can now be effectively addressed through AI solutions. In essence, the key to unlocking the full benefits of AI lies in the ability to redesign operations with AI in mind.
Revealing Invisible Problems
Former United States Secretary of Defense, Donald Rumsfeld, famously distinguished between three types of knowledge: “known knowns,” “known unknowns,” and “unknown unknowns.” While the first two are relatively easy to manage, it’s the third category that poses the greatest challenge. In recent years, however, some companies have begun using artificial intelligence (AI) to uncover these “unknown unknowns” in their businesses. One such company is GNS Healthcare, which applies machine-learning software to identify overlooked relationships among data in patients’ health records and elsewhere. Once a relationship has been identified, the software generates numerous hypotheses to explain it and then suggests which of those are the most plausible. This approach has enabled GNS to uncover a new drug interaction that was previously hidden in unstructured patient notes.
According to CEO Colin Hill, this is not a simple case of data mining to find associations. Rather, GNS’s machine-learning platform is designed to go beyond pattern recognition and correlation, and instead, it is focused on discovering causal links. By doing so, the company is able to offer insights and identify opportunities that would have otherwise remained hidden. In addition, GNS’s platform can be used to predict the effectiveness of different treatments for individual patients, which can help doctors make more informed decisions about their care.
One of the key advantages of AI-powered discovery is that it can help companies navigate complex, multi-dimensional problems that are difficult for humans to unravel. For example, GNS’s platform has been used to identify the root causes of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease, which are influenced by a wide range of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. By analyzing large, diverse data sets, GNS’s software can pinpoint the most important drivers of these conditions and help researchers develop new treatments that target those specific factors.
Overall, the use of AI to uncover “unknown unknowns” is still in its infancy, but the potential benefits are enormous. By helping companies and researchers make sense of complex data sets and identify hidden patterns and insights, these technologies have the potential to transform a wide range of industries and improve the lives of millions of people around the world. As the technology continues to evolve and improve, we can expect to see even more exciting breakthroughs in the years ahead.
Companies should engage in co-creation with stakeholders to develop solutions that involve collaboration with AI systems in order to enhance various processes. For instance, a large agricultural company that aimed to deploy AI technology to assist farmers had access to vast amounts of data on soil properties, weather patterns, historical harvests, and other related factors. The company’s initial plan was to design an AI application that would accurately predict future crop yields. However, before doing so, it was necessary to engage stakeholders in envisioning how they could work with the AI system to achieve this objective.
In the course of engaging with farmers, the organization discovered a more urgent requirement. Specifically, farmers desired a platform that could furnish real-time recommendations on how to enhance productivity. Such recommendations would cover a range of issues, including what crops to cultivate, where to cultivate them, and how much nitrogen to use in the soil. In response to this need, the organization developed an AI system that could provide such advice. The early results of this initiative were encouraging, with farmers expressing satisfaction with the crop yields achieved using the AI’s counsel. The outcomes of this preliminary test were then integrated into the system to improve the algorithms employed. As was the case with the discovery phase, new AI and analytic techniques could support co-creation initiatives, providing suggestions for novel approaches to enhancing processes.
Once a solution has been proposed, the next essential step for companies is to scale it up and then maintain it. A concrete example can be seen in the case of SEB, which initially implemented a version of Aida to aid 15,000 of its bank employees. Subsequently, the company launched the chatbot to its one million customers to further expand its reach.
Through extensive collaboration with numerous companies, we have successfully identified five key attributes of business processes that are often the focus of improvement efforts: flexibility, speed, scale, decision making, and personalization. When undertaking the task of reimagining a particular business process, it is essential to determine which of these traits is the central focus of the desired transformation. Additionally, it is crucial to evaluate how intelligent collaboration can be harnessed to address this area of focus, and identify the necessary realignments and trade-offs with other process characteristics.
Mercedes-Benz integrates cobot arms seamlessly with the human worker’s body, effectively acting as an extension of the said body.
Flexibility.
For Mercedes-Benz executives, inflexible processes presented a growing challenge. Increasingly, the company’s most profitable customers had been demanding individualized S-class sedans, but the automaker’s assembly systems couldn’t deliver the customization people wanted.
In the past, the manufacturing of automobiles has been a rigid and inflexible process that involved the use of automated steps performed by “dumb” robots. However, in order to enhance flexibility, Mercedes-Benz has made the decision to replace some of these robots with AI-enabled cobots and has redesigned its processes to focus on human-machine collaborations. At the company’s plant located near Stuttgart, Germany, cobot arms that are guided by human workers are now responsible for picking up and placing heavy parts, effectively becoming an extension of the worker’s body. This particular system empowers the worker to take control of the build of each vehicle, which entails less manual labour and more of a “piloting” job with the robot. In essence, the collaboration between humans and machines has resulted in a more efficient and flexible car manufacturing process that is more in-line with today’s technological advancements. By incorporating AI-enabled cobots, Mercedes has set an industry standard that other car manufacturers will undoubtedly follow.
The adaptability of the human-machine teams employed by the company is remarkable. The cobots in the manufacturing plant can be reprogrammed with ease using a tablet, and this allows them to handle various tasks depending on the changes in the workflow. This level of agility has been instrumental in helping the manufacturer achieve unprecedented levels of customization. Mercedes, for instance, can personalize vehicle production based on the real-time choices made by consumers at dealerships. This customization can extend to the smallest of details such as the dashboard components, seat leather, and tire valve caps, meaning that no two cars produced at the Stuttgart plant are identical. The company’s use of technology has revolutionized the manufacturing process and is a testament to the benefits that can be derived from the effective integration of human and machine labor.
Enhancing Performance
In various industries, artificial intelligence and human beings are working together at different organizations.
Speed.
In certain business practices, the emphasis is placed on expediency. One such procedure pertains to identifying instances of credit-card deceit. Corporations are constrained to a mere matter of seconds to discern whether or not they should authorize a specific transaction. In the event that it is determined to be fraudulent, the company will probably have to absorb the associated loss. However, if they decline a lawful transaction, they forfeit the fee from that sale and potentially alienate the customer. As a result, it is imperative for companies to possess a system that can quickly differentiate between legitimate and fraudulent credit-card activity.
HSBC, among other major banks, has developed an AI-driven solution that amplifies the speed and precision of fraud detection. By scrutinizing millions of transactions every day, the AI analyzes data relating to purchase location, customer behavior, IP addresses, and other relevant factors to identify any subtle patterns that may indicate possible fraud. Initially implemented in the United States, the system proved to be highly effective in reducing the incidence of undetected fraud and false positives. After this success, HSBC introduced the system across the UK and Asia. Similarly, Danske Bank has also implemented a distinct AI system that has significantly improved its rate of fraud detection by 50% and reduced false positives by 60%. The reduction in the number of false positives enables investigators to focus their attention on transactions flagged by the AI that require human judgment due to equivocal circumstances. Overall, these AI-powered systems have been instrumental in streamlining the process of fraud detection and mitigating its adverse effects.
The battle against financial fraud can be likened to an ongoing arms race, as improved detection methods prompt criminals to devise more sophisticated tactics, necessitating further advancements in detection capabilities. This constant cycle demands that algorithms and scoring models utilized in the fight against fraud have a very brief lifespan, requiring routine updates. Furthermore, different countries and regions adopt different models, further complicating the situation. As a result, a vast army of data analysts, IT professionals, and financial fraud experts is essential at the intersection of humans and machines to ensure that the software stays one step ahead of the criminals. Only through the tireless efforts of these professionals can we hope to stay ahead of the ever-evolving threat of financial fraud and protect the financial well-being of individuals and organizations worldwide.
Scale.
Poor scalability can often be a major hindrance to the improvement of various business processes, especially those that rely heavily on human labor with very little machine assistance. Take, for instance, the employee recruitment process at Unilever, a consumer goods behemoth with a 170,000-strong workforce. The HR department identified a need to diversify the workforce by focusing on entry-level hires and then promoting the best performers to management positions. However, the company’s existing processes were unable to effectively assess a large number of potential candidates while still providing each one with individual attention. As a result, the company was struggling to attract a diverse pool of exceptional talent.
This is a common problem for companies that rely too heavily on manual processes, as these often struggle to scale efficiently. In today’s fast-paced business world, organizations need to be able to quickly and effectively evaluate potential candidates in order to stay competitive. This requires the implementation of more streamlined, automated processes that can handle larger volumes of candidates without sacrificing the quality of evaluation. By doing so, companies can ensure that they are attracting and retaining top talent, which is essential for long-term success.
Fortunately, many companies are starting to recognize the importance of automation in their recruitment processes. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence, these companies are able to automate many of the more tedious tasks involved in recruiting, freeing up HR personnel to focus on more strategic activities. This not only improves the efficiency of the recruitment process, but also enhances the candidate experience, which is critical for building a strong employer brand. Ultimately, by investing in scalable, automated recruitment processes, companies can position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly competitive business landscape.
Unilever has successfully integrated artificial intelligence (AI) with human capabilities to streamline the recruitment process. In the initial round of the application process, candidates are asked to participate in online games that evaluate their risk aversion and other traits that are important for the specific position. These games don’t have any right or wrong answers, but their outcomes assist Unilever’s AI in identifying the individuals who are best suited for the job. In the next round, applicants are required to submit a video in which they answer questions tailored to the position they are interested in. The AI not only assesses their answers but also considers their body language and tone. The AI then selects the top candidates for in-person interviews at Unilever. Finally, the human recruitment team makes the final hiring decisions. This hybrid approach has enabled Unilever to identify the best candidates while saving time and resources.
The effectiveness of the new recruitment process in terms of producing better quality employees cannot be determined at this point in time. The company has been diligently monitoring the performance of the new hires, yet more information is still required to make an accurate assessment. Nevertheless, it is evident that the new system has significantly expanded the scope of Unilever’s recruitment efforts. This is partly due to the system being easily accessible through smartphones, which has resulted in a doubling of the number of applicants to 30,000 within a year. Additionally, the number of universities represented has increased from 840 to 2,600, and the socioeconomic diversity of new hires has also improved. Furthermore, the average time taken to make a hiring decision has been reduced from four months to just four weeks, and the amount of time recruiters spend reviewing applications has fallen by a remarkable 75%.
Decision making.
AI has the potential to enhance decision-making skills of employees by offering personalized information and guidance, which can be immensely beneficial. This technology can be particularly advantageous for employees working in operative positions where the accuracy of decisions can significantly affect the organizational outcomes. By leveraging AI, employees can be equipped with the right set of tools to make better-informed decisions that align with the company’s goals and values.
The utilization of digital twins, which are virtual representations of physical equipment, has greatly improved equipment maintenance. General Electric, for instance, has developed software models of its turbines and other industrial products, and constantly updates them with operating data that is streamed from the equipment. This has enabled the company to accumulate a vast amount of information on both normal and abnormal performance by gathering readings from numerous machines in the field. With the application of machine-learning algorithms, GE’s Predix software is capable of predicting the failure of specific parts in individual machines. This technology has revolutionized the way in which equipment maintenance is conducted, allowing for predictive maintenance that can prevent equipment failures and reduce downtime. The use of digital twins has clearly demonstrated their immense potential to optimize industrial processes and reduce costs.
The utilization of this innovation has brought about a fundamental transformation in the decision-making process that is required to maintain industrial equipment. For instance, Predix is capable of detecting any unexpected rotor wear and tear that may exist in a turbine. It can also analyze the operational history of the turbine, determine that the damage has increased four times over the past few months, and alert the concerned parties that the rotor may lose up to 70% of its useful life if no action is taken. Furthermore, the system can provide recommendations on appropriate measures to be taken based on the current state of the machine, the operating environment, and other aggregated data concerning similar damage and repairs to other machines. Additionally, Predix can produce information on the associated costs and financial benefits of its recommendations, as well as provide a confidence level of 95% for the assumptions used in its analysis. All of these features make Predix an invaluable tool for maintaining industrial equipment.
Thanks to Predix, maintenance staff are now able to detect rotor damage early on, which would have otherwise gone unnoticed during routine maintenance inspections. Without such early detection, the rotors would have failed, resulting in costly shutdowns. By using Predix, maintenance personnel are now notified of potential issues before they worsen, and they have access to the necessary information to make informed decisions that can save GE millions of dollars. As a result, Predix has undoubtedly proven to be a valuable asset to GE’s maintenance and operations management.
Personalization.
Providing customers with personalized and tailor-made brand experiences has always been the ultimate goal of marketing. However, with the ever-evolving technology, particularly with AI, the level of personalization has reached new heights, which was previously unimaginable. A perfect example of this lies in the music streaming service Pandora, which uses AI algorithms to generate personalized playlists for millions of users based on their preferences in songs, artists, and genres. Another instance is Starbucks, which has been using AI to recognize customers’ mobile devices, accessing their ordering history, and making personalized recommendations to the baristas. This AI-powered technology has been sifting through and processing vast amounts of data to suggest specific offerings or actions, while the human element of intuition and judgment is still crucial in making the final decision or selecting the best option from a set of choices. In a nutshell, AI has revolutionized the field of marketing by offering a level of personalization that was once impossible to achieve, and it has encouraged brands to focus on delivering a unique and individual experience to their customers.
The utilization of AI by the Carnival Corporation to customize the cruise experience for millions of vacationers is being facilitated through a wearable device called the Ocean Medallion and a network that enables smart devices to connect. The data flowing from the medallion and from sensors and systems throughout the ship is dynamically processed by machine learning to assist guests in getting the most out of their vacations. The medallion simplifies the boarding and debarking processes, tracks guests’ activities, simplifies purchasing by connecting their credit cards to the device, acts as a room key and also connects to a system that foresees guests’ preferences, enabling crew members to deliver personalized service to each guest by suggesting tailored itineraries of activities and dining experiences. With the use of AI, guests can now experience an unparalleled level of comfort and convenience, which further enhances their overall vacation experience, thereby leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty. This innovative use of technology is a game-changer in the cruise industry, providing a roadmap for others to follow in terms of leveraging AI to personalize the customer experience.
The demand for fresh job positions and skilled individuals is crucial in today’s workforce.
Re-envisioning a business process goes beyond simply integrating AI technology; it necessitates a significant dedication to cultivating employees with what we term “fusion skills” – abilities that enable them to function effectively at the human-machine junction. Initially, individuals must understand how to delegate responsibilities to the new technology, such as when doctors rely on computers to assist them in interpreting X-rays and MRIs. Furthermore, staff should be aware of how to blend their unique human talents with those of an intelligent machine to achieve a superior outcome than either could produce alone, as seen in robot-assisted surgery. Employees must have the ability to teach intelligent agents new skills and receive training to function effectively within AI-enhanced processes. All of these abilities are critical components of the fusion skills required to successfully implement AI technology within a business process.
In order to effectively obtain the information they require from an AI agent, individuals must possess knowledge on the most appropriate way to ask questions. Additionally, it is crucial for companies to have dedicated employees, such as those belonging to Apple’s differential privacy team, who are responsible for ensuring the ethical and lawful use of their AI systems. By having these measures in place, organizations can guarantee that the application of AI technology aligns with their values and is conducted in a socially responsible manner.
In the coming years, we anticipate a transformation in the way companies structure their roles, with a focus on the desired outcomes of reimagined processes. There will be a shift towards organizing corporations around various skill sets instead of the traditional, inflexible job titles. AT&T has already taken steps in this direction, as it transitions from landline telephone services to mobile networks and endeavors to retrain 100,000 employees for new positions. As part of this initiative, the company has overhauled its organizational chart by streamlining approximately 2,000 job titles into a smaller number of broader categories that encompass similar skills. Some of these skills are more predictable, such as proficiency in data science and data wrangling, while others are less obvious, like the ability to use simple machine-learning tools to cross-sell services. This restructuring will enable companies to be more nimble and adaptive, catering to the ever-evolving needs of the modern business landscape.
CONCLUSION
Most operations that involve human-machine interaction necessitate individuals to perform novel and distinct duties, such as coaching a chatbot, and to execute tasks in a different manner, such as utilizing that chatbot to furnish superior customer service. Nevertheless, we have only observed a few companies in our research surveys that have commenced reimagining their business processes to optimize collaborative intelligence. The takeaway is quite evident: enterprises that utilize machines solely to replace employees through automation will fail to leverage the complete potential of artificial intelligence. Such a strategy is fundamentally flawed. The future leaders will be the ones who wholeheartedly embrace collaborative intelligence, enhancing their operations, markets, industries, and, most importantly, their labor force.
ANOTHER Edition of this write-up was featured in the July-August 2018 issue (pp. 114-123) of the prestigious Harvard Business Review.
- James Wilson holds the position of Global Managing Director of Thought Leadership & Technology Research at Accenture and has coauthored several books, including “Radically Human: How New Technology Is Transforming Business and Shaping Our Future” (Harvard Business Review Press, 2022) and “Human + Machine: Reimagining Work in the Age of AI” (Harvard Business Review Press, 2018).
- Paul Daugherty is the Group Chief Executive – Technology and CTO at Accenture and has also coauthored the aforementioned books. The publications are highly acclaimed and have been lauded for their insightful analysis of technology and business transformation. Wilson and Daugherty are both recognized experts in their fields, and their extensive experience and knowledge have made them sought after speakers and consultants. Their contributions to the field of technology research and innovation have been significant and influential, and they continue to inspire and educate the next generation of thought leaders in the industry.
[1] Siri is Apple’s virtual assistant for iOS, macOS, tvOS and watchOS devices that uses voice recognition and is powered by artificial intelligence (AI).
[2] Dreamcatcher is a cloud-based 3D design software that grants designers the ability to programmatically optimize 3D CAD designs.