Menu
The Purpose of this paper is to overview the Logistics/Logistics management in supply chain and their current logistics related issue in a present day business and present a conceptual methodology for related issue. The methodology based on the logistics, which are inputs for the methodology and benefits which are output of methodology. A literature review is conducted on key external and internal issue of logistics and also logistics issue in industry, and determines its various dimensions. Based on the insights gained, a conceptual methodology for logistics issue Present. The information flow in the conceptual methodology is bi- directional at all levels.
The present corporate job is very challenging. Every business has to face competitions from multiple dimensions and directions. As explained by Michael Porter the business in 21st century can survive and succeed only if it is able to fulfill the challenges of the present demands regarding logistics. History repeats where the business which is not able to provide proper logistics for its products and supply the product to ultimate consumer has lost its reputation in the business world. However good the product is if it would survive the competition and reaches the ultimate consumer in time it is demanded for [1].
Since the early 1990′s, the business outlook has changed. Due to the globalization, the competition has demanded the customer should get the right material, at the right time, at the right point and in the right condition at the lowest cost. Outsourcing logistics functions enables a company to focus on its core By doing so, the companies can best utilize their resources, allowing a world class solution provider to professionally manage their logistics, leveraging their technology and staff infrastructure. Logistics has become a part and parcel for every business today. No business with marketing, manufacturing or project execution can succeed without logistics support [1].
The paper makes an attempt to understand the importance of logistics, Logistics issue and then to present a conceptual methodology for logistics issue. The objective of this paper are- (1) to understand the concepts of logistics and logistics management in supply chain. (2) To highlight the logistics issue in current logistics system.
(3) To highlight various issue in logistics industry. (4) To present a conceptual methodology for related issue. The paper is organized as after the literature review a conceptual methodology for logistics related issue is presented. Finally, concluding remarks with some directions for future research are provided [2].
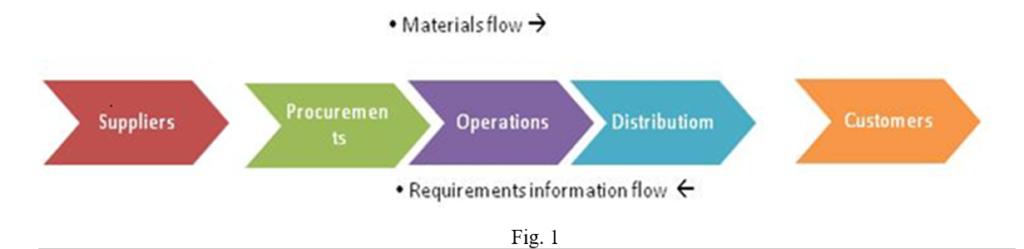
is defined as “Planning implementing and controlling the physical flow of material and finished goods from point of origin to point of use to meet customer`s need at a profit” by “Philip Kotler” It is essentially a planning process and an information activity So it is a integrative process that optimizes the flow of material and supplies through the organization and its operations to the customer as shown in below Fig 1.
The word logistic has originated from Greek word ‘Logistikos’ and the Latin word ‘Logisticus’ which means science of computing & calculating. During World War II logistics gained importance in army operations covering the movement of food, medicines, men & equipment across the border. Today it has acquired a broader meaning and is used in the business for the movement of material from suppliers to the manufacturer and finally the finished.
Logistic is ‘the part of the supply chain management that plans, implements, and controls the efficient, effective forward an reverse flow and storage of goods, services and related information between the point of origin and the point of consumption in order to meet customers’ requirements [1].According to Stern and El-Ansary (1988), ‘the term Logistics Management encompasses the total flow of materials, from acquisition of raw materials to the delivery of the finished product to the ultimate consumer and the counter-flow of information that controls and records the material movement’ [1].Logistics embodies the effort to deliver: the right production the right quantity in the right condition to the right place at the right time for the right customer at the right cost.
Primary process are Setting customer services goals, Transportation, Inventory management, Location and Secondary, or Supporting are Warehousing, Materials handling, Acquisition(Purchasing), Protective Packaging, Product Scheduling, Order Processing etc.
is the part of Supply chain management that plans, implements and controls the efficient, effective, forward, and reverse flow and storage of goods, services, and related information between the point of origin and the point of consumption in order to meet customer’s requirements. It involves the integration of information, transportation, inventory, warehousing, material handling and packaging, and occasionally security.
is defined as a system of organizations, people, activities, information, and resources involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer. Supply chain activities involve the transformation of natural resources, raw materials, and components into a finished product that is delivered to the end The network of organizations that are involved, through upstream and downstream linkages, in the different processes and activities that produce value in the form of products and services delivered to the ultimate consumer [3].A set of firms that pass materials forward. The alignment of firms that brings products or services to market including the final customers as part of the supply chain [2].A set of three or more entities (organizations or individuals) directly involved in the upstream and downstream flows of products, services, finances, and/or information from a source to a customer [4].Logistics is part of supply chain or supply chain management whose totally focus on material flow from supplier to customer and information flow from customer to supplier.
Cycle view – In which the processes in a supply chain are divided into a series of cycles, each performed at the interface between two successive stages of a supply chain (Fig 2.2).

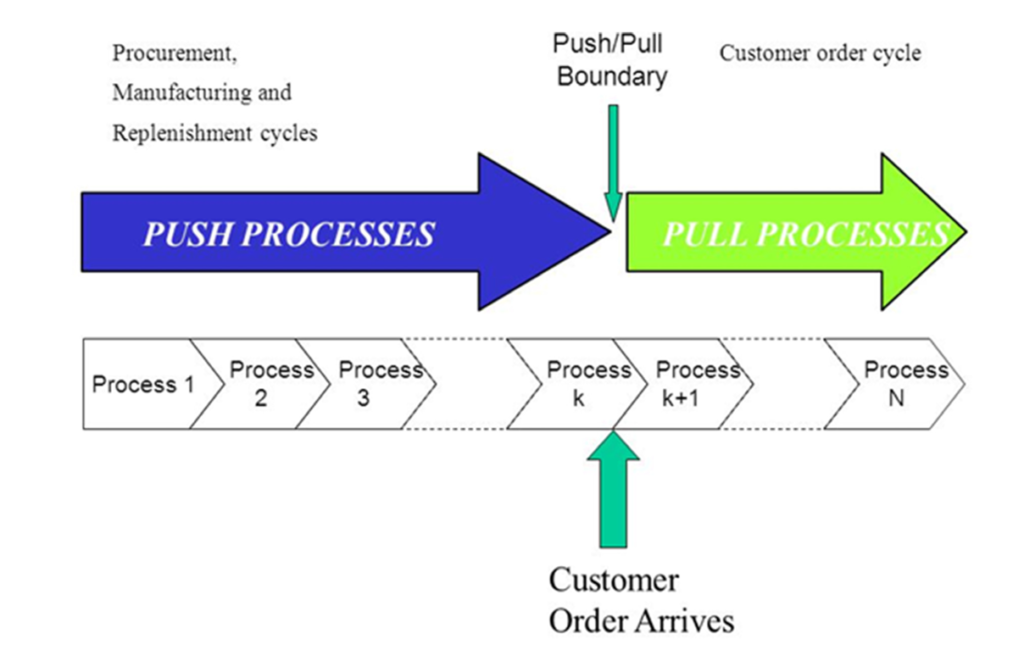
In which the processes in a supply chain are divided into two categories depending on whether they are executed in response to a customer order or in anticipation of customer orders. Pull processes are initiated by a customer order, whereas push processes are initiated and performed in anticipation of customer orders (Fig 2.3) [5].
There are several factors and costs that affect logistics. These issues may be listed as:
The paper presents a conceptual methodology for logistics issue. The key logistics issue is here mentioned depending its internal or external logistics issue .It is expected that this methodology would be highly beneficial to the organizations in leveraging the efficiency of supply chain management. There is a need for an empirical validation of the proposed methodology. The bi-directional information at different levels will have affected the supply chain at all levels and it should be managed to reduce the information distortions. Logistics is an important area where every company has to concentrate on and differentiate themselves with their competitors. With the growing demand for various varieties of products available all over the world people’s expectations are changing for every product. If a company wants to survive in the long run it should pay special attention to the area of supply chain and logistics. Research is demanded to reduce the product cost and improve the quality with reduced delivery time.
Maadico is an international consulting company in Cologne, Germany. This company provides services in different areas for firms so they will be able to interact with each other. But specifically, raising the level of knowledge and technology in various companies and assisting their presence in European markets is an aim for which Maadico has developed … (Read more)